Legislative Processes and Societal Influence
Understanding how laws are made and enforced is fundamental to comprehending the structure of any society. Legislative processes are intricate systems through which rules are formulated, debated, and enacted, ultimately shaping the daily lives of citizens. These processes are not isolated events but are deeply intertwined with the social, economic, and political fabric of a nation, reflecting its values and aspirations while also addressing its challenges. This exploration delves into the mechanics of lawmaking and its profound impact on public life.
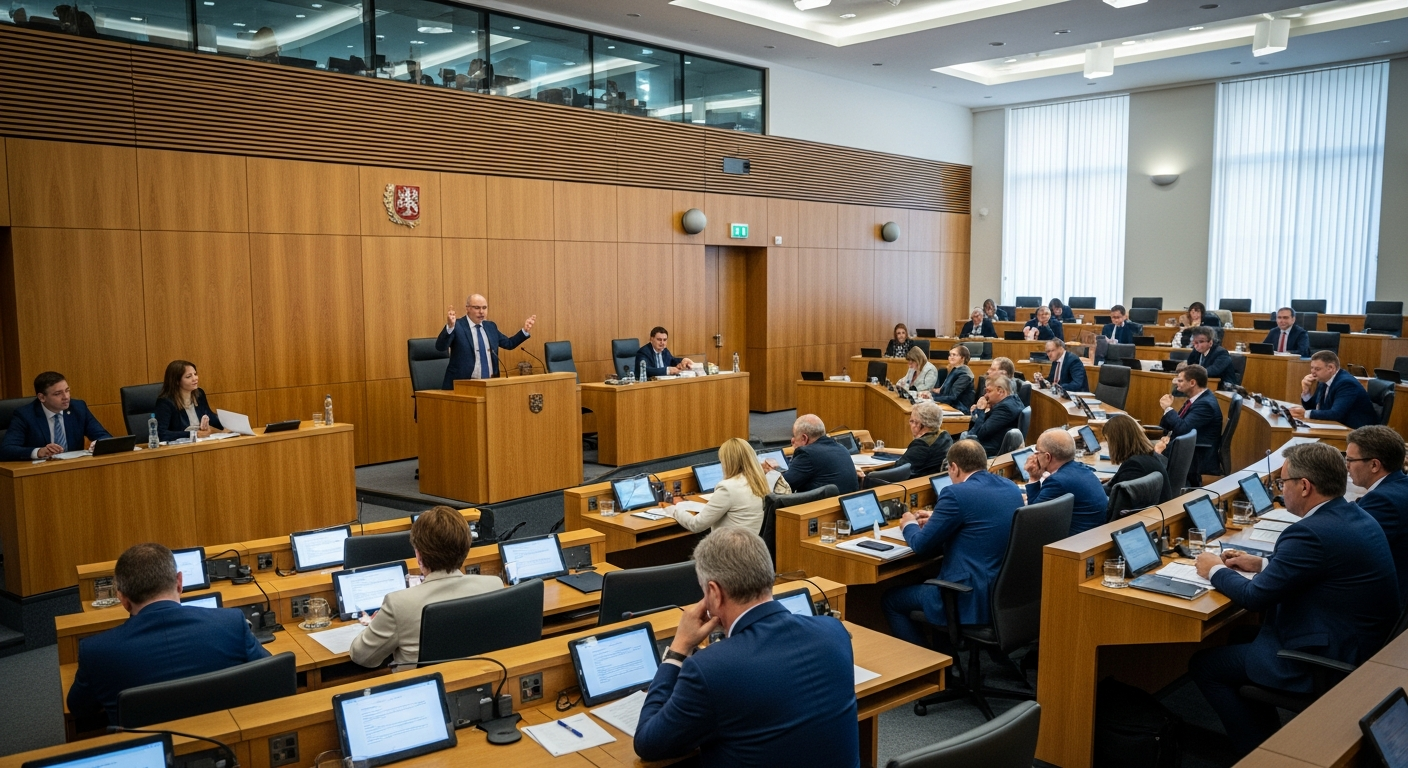

How is Legislation Developed?
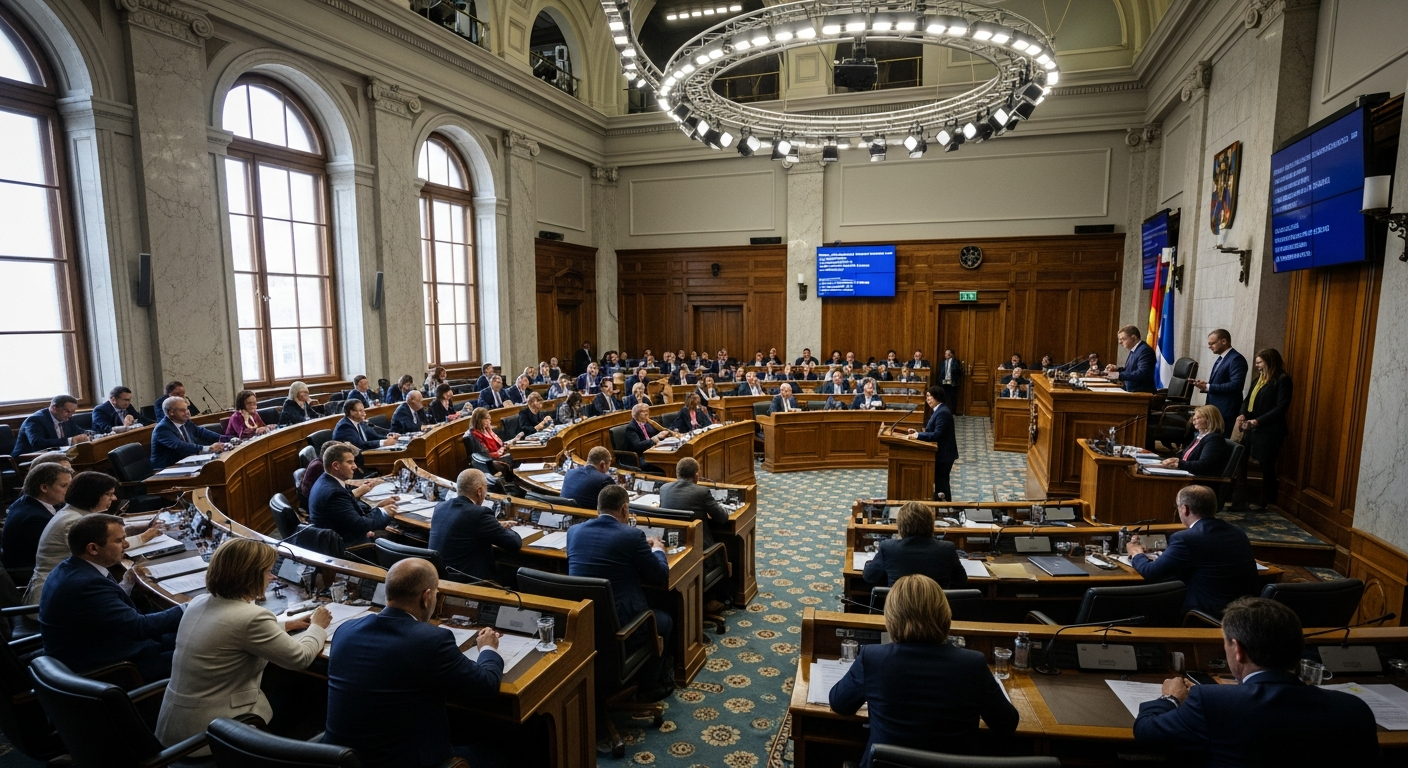
Legislation is the primary mechanism through which governments establish rules and regulations for their jurisdictions. The development of a new law typically begins with an idea, which can originate from various sources, including public petitions, government agencies, or political parties. This idea is then drafted into a bill, often by legal experts, before being introduced into the legislative body, such as a Parliament or Congress. The bill undergoes several stages of review, debate, and amendment within committees and on the legislative floor. This rigorous process allows for diverse perspectives to be heard and considered, ensuring that the proposed law is thoroughly scrutinized before it proceeds. Once passed by both houses (in bicameral systems) and approved by the Executive branch, typically the head of state or government, it officially becomes law, impacting the entire legal framework.
What Role Do Policy and Regulation Play?
Policy and Regulation are critical components of governance that extend beyond the initial act of creating a statute. While legislation sets the broad legal framework, policies provide more detailed guidelines and objectives for how those laws should be implemented and achieved. Regulations, on the other hand, are specific rules developed by government agencies under the authority of existing legislation to govern particular activities or sectors. These regulatory frameworks ensure compliance with legal mandates and often address technical, environmental, or economic standards. Effective governance relies on a coherent interplay between overarching legislation, strategic policies, and detailed regulations to maintain order, protect public interests, and foster societal development.
How Does Justice and the Judiciary System Function?
Justice is a cornerstone of any democratic society, and the Judiciary system is tasked with interpreting and applying the laws established through the legislative process. This branch of government, comprised of Courts and judges, ensures that laws are administered fairly and impartially. When disputes arise regarding the interpretation of a statute, or when an individual is accused of violating a legal provision, the courts provide a forum for resolution. Through trials, hearings, and appeals, the judiciary upholds the rule of law, protects individual Rights, and ensures that all citizens are subject to the same legal standards. The independence of the judiciary is crucial for maintaining public trust and safeguarding the integrity of the legal system.
Understanding Civic Rights and Citizen Participation
Civic engagement and the protection of individual Rights are vital for a healthy Democracy. Citizens play a crucial role not only in electing their representatives who craft legislation but also in holding them accountable. Public participation can manifest in various forms, including advocacy, protests, and providing input during public consultations on proposed laws and policies. The Constitution typically outlines fundamental rights, such as freedom of speech, assembly, and the right to a fair trial, which empower individuals to participate meaningfully in their governance. These rights ensure that the voices of the people are heard and considered throughout the legislative and administrative processes, reinforcing the democratic ideal that power ultimately resides with the citizen.
The Importance of Ethics and Compliance in Administration
Effective Administration of laws and policies requires a strong commitment to Ethics and Compliance within government bodies. Public servants are expected to act with integrity, transparency, and accountability in their duties. Ethical guidelines help prevent corruption, ensure fair decision-making, and maintain public trust. Compliance refers to adherence to all applicable laws, regulations, and internal policies. Government agencies establish robust compliance frameworks to ensure that their operations meet legal standards and that public resources are used responsibly. Upholding ethical standards and ensuring compliance are essential for the credibility and effectiveness of any system of governance.
Constitutional Frameworks and Statutes
Every nation operates under a foundational set of principles, often codified in a Constitution, which serves as the supreme law of the land. The Constitution defines the powers and responsibilities of the different branches of government—Legislative, Executive, and Judiciary—and establishes the fundamental rights and freedoms of its citizens. All other laws, known as Statutes, must conform to the provisions of the Constitution. Statutes are specific laws passed by the legislative body on a wide range of subjects, from criminal offenses to environmental protection. The constitutional framework provides stability and a clear hierarchy for the entire legal system, ensuring that all legislative actions align with the nation’s core values and governance structure.