The Evolution of Vehicle Design and Aerodynamics
The journey of vehicle design is a compelling narrative of human ingenuity, evolving from rudimentary horseless carriages to the sophisticated machines of today. This transformation has been driven by a relentless pursuit of efficiency, safety, and aesthetic appeal. Central to this evolution is the understanding and application of aerodynamics, a discipline that shapes how vehicles interact with air, influencing everything from speed and fuel consumption to stability and interior comfort. As automotive engineering continues to advance, the interplay between form and function becomes ever more critical, pushing the boundaries of what is possible on roads worldwide.

Early Automotive Design and Engineering Principles
In the nascent stages of the automotive industry, early vehicle design was largely influenced by carriage-making traditions. Functionality and structural integrity were paramount, with less emphasis placed on aerodynamic considerations. Vehicles were often boxy, tall, and heavy, reflecting the manufacturing capabilities and prevailing engineering knowledge of the time. The primary goal was to create a reliable mode of transport, and early engines, while revolutionary, did not demand the sleek forms seen today. As speeds increased, however, the limitations of these designs became apparent, paving the way for a more scientific approach to vehicle development.
The Role of Aerodynamics in Vehicle Performance
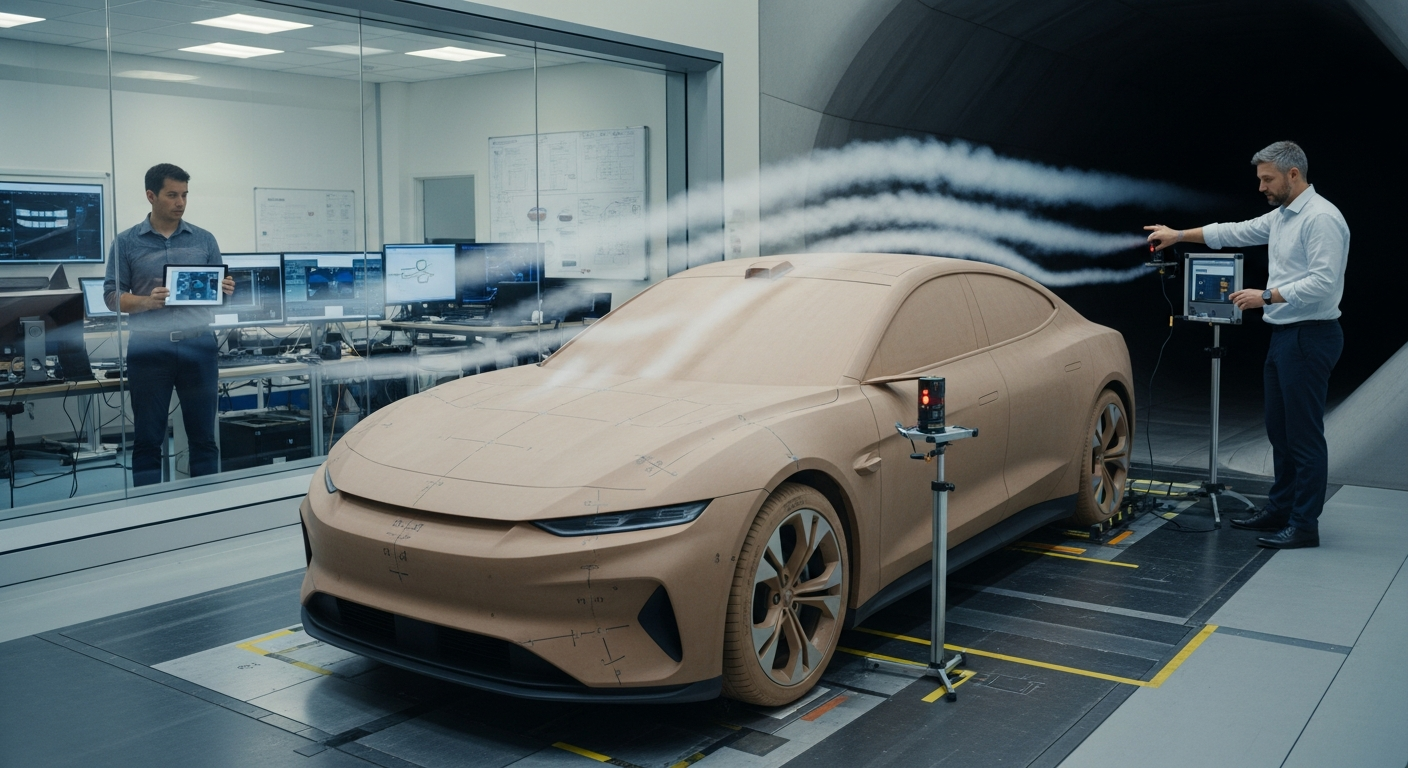
The recognition of air resistance as a significant factor in vehicle performance marked a turning point in automotive design. Aerodynamics, the study of how air flows around objects, became crucial for improving speed, fuel efficiency, and stability. Designers began to experiment with more streamlined shapes, curved surfaces, and reduced frontal areas to minimize drag. This shift was not merely aesthetic; it was a fundamental engineering challenge aimed at optimizing the vehicle’s interaction with its environment. Innovations like teardrop shapes and integrated fenders were early examples of applying aerodynamic principles to enhance the driving experience and reduce the power required from engines.
Advancements in Materials and Manufacturing
The evolution of vehicle design has been intrinsically linked to advancements in materials and manufacturing processes. Historically, steel dominated vehicle construction, offering strength and durability. However, the drive for lighter, stronger, and more sustainable vehicles has led to the widespread adoption of materials like aluminum alloys, carbon fiber composites, and advanced high-strength steels. These materials allow for complex shapes that improve aerodynamics and structural integrity while reducing overall weight. Modern manufacturing techniques, including advanced stamping, robotic assembly, and 3D printing, have also enabled greater precision and design freedom, transforming innovative concepts into tangible vehicles with improved automotive characteristics.
How Design Enhances Safety and User Experience
Beyond performance, vehicle design plays a critical role in enhancing safety and the overall user experience. Contemporary design integrates passive safety features such as crumple zones, reinforced passenger cells, and strategically placed airbags, all of which are meticulously engineered to protect occupants in a collision. Active safety systems, supported by advanced technology and connectivity, also influence design by requiring precise sensor placement and integrated displays. Furthermore, interior design focuses on ergonomics, intuitive controls, and comfortable layouts, transforming the vehicle cabin into a more engaging and functional space for modern mobility. This comprehensive approach underscores the innovation in making vehicles not just faster or more efficient, but also safer and more enjoyable to drive.
Influence of Electric and Autonomous Technologies on Future Design
The advent of electric and autonomous vehicle technologies is profoundly reshaping the future of vehicle design. Electric powertrains, with their compact components and absence of traditional engines, offer designers unprecedented freedom to reimagine vehicle proportions and interior layouts. This allows for flatter floorboards, larger cabins, and new storage solutions. Autonomous driving capabilities further push this boundary, potentially transforming vehicles from mere modes of transport into mobile living or working spaces. The focus shifts from the driver to the occupants, fostering designs that prioritize comfort, connectivity, and versatile interior configurations. Sustainable design practices are also gaining prominence, emphasizing recyclable materials and energy-efficient manufacturing processes, aligning with broader environmental goals for urban and global transport systems. These innovations are set to redefine our relationship with vehicles and roads.