Understanding International Judicial Systems
International judicial systems represent a complex network of courts, tribunals, and legal frameworks designed to address disputes and uphold justice beyond national borders. These systems play a crucial role in maintaining peace, enforcing international law, and protecting human rights across the globe. Their establishment reflects a collective effort by states to create mechanisms for resolving conflicts peacefully and ensuring accountability for actions that transcend national jurisdiction. Exploring these intricate structures offers insight into global governance and the evolving landscape of international relations, highlighting how diverse legal traditions converge to address shared challenges and promote a more ordered world.
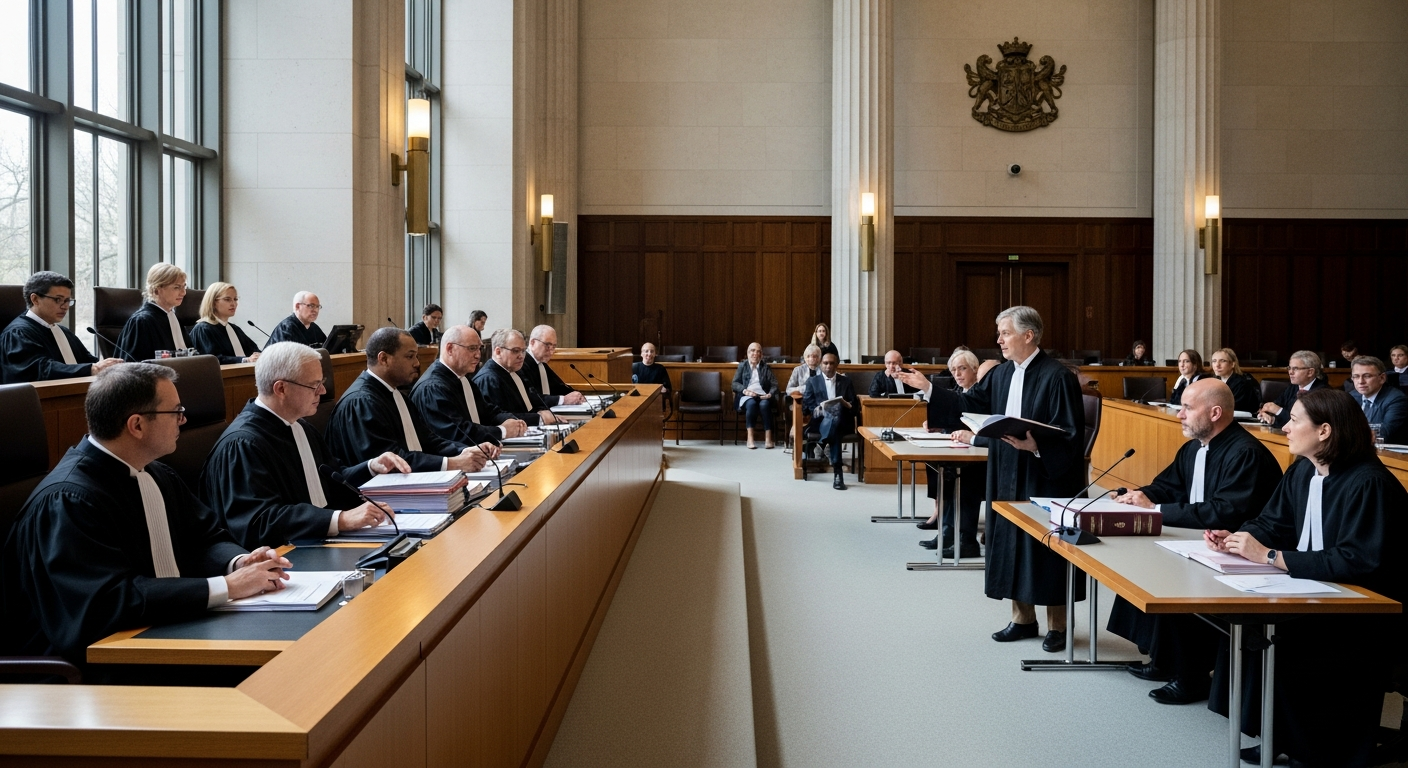

The global landscape of law and governance is significantly shaped by international judicial systems, which are essential for upholding principles of justice and ensuring adherence to global policy and regulation. These systems operate independently of national courts, addressing a wide array of issues from human rights violations to trade disputes and war crimes. Their existence underscores a commitment by the international community to establish a rule of law that extends beyond individual state boundaries, fostering stability and cooperation among nations. Understanding their function is key to comprehending how international relations are managed and how global norms are enforced.
The Foundations of International Law and Justice
International judicial systems are built upon a foundation of international law, which includes treaties, conventions, customary international law, and general principles of law. These sources guide the decisions of international courts and tribunals. The concept of civics at an international level involves understanding the rights and responsibilities of states and individuals within this global legal framework. Protecting fundamental rights is a primary objective, with international legislation often aiming to safeguard individuals from abuses that national systems might fail to address. This framework provides avenues for redress and accountability, contributing to a more equitable global society.
Structure and Function of International Judicial Bodies
The judiciary at the international level comprises various courts and tribunals, each with specific jurisdictions and mandates. Examples include the International Court of Justice (ICJ), the International Criminal Court (ICC), and regional courts like the European Court of Human Rights. These bodies interpret and apply international law, often drawing upon constitutional principles that underpin their establishment and operation. Effective global governance relies on the credibility and impartiality of these institutions, which must navigate complex political landscapes while upholding legal standards. Their judgments contribute to the progressive development of international law.
Diplomacy, Administration, and Ethical Considerations
The operation of international judicial systems is deeply intertwined with diplomacy and international relations. While courts strive for independence, political realities can influence their effectiveness and the enforcement of their decisions. The administration of these courts involves intricate procedural rules and the management of complex cases, often involving multiple states and diverse legal traditions. Ethics play a critical role, ensuring that judicial processes are fair, transparent, and free from bias. The application of international statutes and principles of jurisprudence requires careful consideration of universal values and the specific circumstances of each case, balancing legal rigor with practical implications.
Sovereignty, Treaties, and Global Accountability
A critical tension in international law lies between state sovereignty and the jurisdiction of international courts. While states are generally considered sovereign within their borders, they voluntarily cede some authority by signing and ratifying international treaties. These agreements form the basis for much of international law and the jurisdiction of judicial bodies. The pursuit of accountability for serious international crimes or violations of international law is a central function of these systems, aiming to deter future offenses and provide justice for victims. The role of advocacy by non-governmental organizations and other actors is often crucial in bringing cases before these courts and ensuring that justice is pursued.
The Role of International Judicial Systems in Global Stability
International judicial systems are pivotal in fostering global stability by providing peaceful mechanisms for dispute resolution. They promote citizenship in a broader sense, encouraging adherence to international norms and fostering a shared understanding of rights and responsibilities. By upholding democracy and the rule of law on a global scale, these institutions contribute to preventing conflicts and addressing their root causes. Their work ensures that international law is not merely theoretical but a practical instrument for managing global challenges and advancing human dignity. The ongoing evolution of these systems reflects a continuous effort to adapt to new global realities and strengthen the international legal order.
International judicial systems are fundamental pillars of global governance, offering avenues for resolving disputes, enforcing international law, and promoting accountability. They represent a significant achievement in human cooperation, demonstrating a collective commitment to peace, human rights, and the rule of law across borders. While facing inherent challenges related to enforcement and political will, their continued development and function remain vital for navigating the complexities of an interconnected world and ensuring a more just global society.