Vehicle Aerodynamics and Fuel Efficiency Principles
Vehicle aerodynamics plays a crucial role in determining a car's performance and, significantly, its fuel efficiency. Understanding how air interacts with a vehicle's body at speed is fundamental to modern automotive engineering, influencing everything from design aesthetics to the practical costs of daily transport. This field continually evolves, driven by the persistent demand for more economical and environmentally conscious vehicles across all segments of mobility.
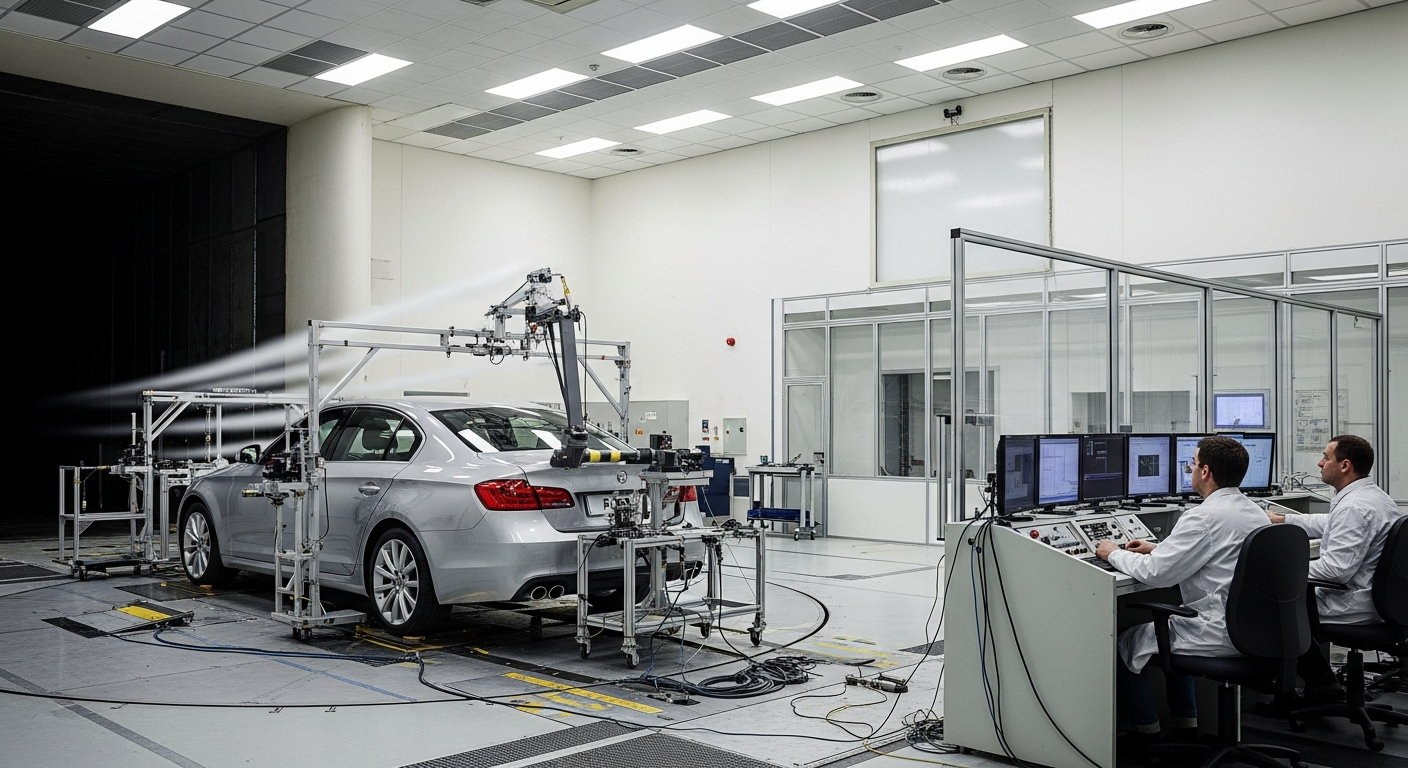

Understanding Aerodynamics in Automotive Engineering
The study of aerodynamics, a fundamental branch of fluid dynamics, meticulously analyzes the movement of air and its intricate interactions with moving objects. In the realm of automotive engineering, this translates to a comprehensive examination of how air flows around a vehicle, meticulously identifying and quantifying the forces it generates. Primarily, these forces are drag and lift. Drag is a resistive force that directly opposes a vehicle’s forward motion, necessitating greater energy expenditure—and consequently, more fuel—to overcome. Lift, while generally less impactful for passenger cars compared to aircraft, can still influence vehicle stability and tire grip, especially at elevated speeds. Engineers employ advanced methodologies, including sophisticated wind tunnels for physical testing and computational fluid dynamics (CFD) simulations, to meticulously model and refine vehicle shapes. The ultimate goal is to minimize the drag coefficient, a critical metric directly correlating with improved overall vehicle efficiency and reduced fuel consumption. This rigorous process is an indispensable component in the development of both traditional internal combustion engine vehicles and the latest electric and hybrid automotive designs.
Impact of Vehicle Design on Fuel Efficiency
The external form and contours of a vehicle are far more than mere aesthetic choices; they represent a critical determinant of its aerodynamic performance and, by extension, its fuel efficiency. Designs characterized by smooth, uninterrupted lines, a carefully tapered rear section, and a minimized frontal area are all meticulously crafted elements aimed at significantly reducing air resistance. A clear historical progression illustrates this, with the transition from the more angular, boxy car and truck designs of previous decades to the sleeker, more streamlined profiles prevalent today, driven largely by the imperative for enhanced fuel economy. Furthermore, subtle yet impactful features such as flush-mounted door handles, seamlessly integrated spoilers, and optimized underbody panels play a crucial role in managing airflow, thereby mitigating turbulence and flow separation. Even seemingly minor details, including the precise angle of the windshield or the sculpted form of side mirrors, collectively contribute to the vehicle’s overall drag coefficient, directly influencing the amount of fuel or energy required for propulsion during routine driving.
Technological Advancements in Aerodynamic Design
Innovation within automotive design is a continuous endeavor, persistently striving to advance the frontiers of aerodynamic efficiency. Contemporary technology has enabled the integration of sophisticated active aerodynamic systems into modern vehicles. Examples include active grille shutters, which intelligently open or close to regulate engine cooling and optimize airflow over the front of the vehicle, and adaptive spoilers, which dynamically adjust their angle based on vehicle speed to balance downforce requirements with drag reduction. For the rapidly expanding segment of electric and hybrid vehicles, where maximizing range is often a paramount concern, achieving superior aerodynamic efficiency is even more critical. Designers are increasingly incorporating advanced lightweight materials and employing complex geometric forms, sometimes drawing inspiration from natural structures through biomimicry, to craft shapes that cleave through the air with minimal resistance. These continuous technological advancements are indispensable for extending the operational range of battery-electric vehicles and for significantly reducing the overall energy consumption of all contemporary vehicle types.
Aerodynamics and Driving Dynamics
Beyond the direct influence on fuel efficiency, aerodynamics profoundly impacts a vehicle’s driving dynamics, stability, and overall safety, particularly at higher operational speeds. Effective airflow management contributes significantly to enhanced vehicle stability, a noticeable reduction in wind noise within the cabin, and improved handling characteristics. Vehicles exhibiting suboptimal aerodynamic profiles may experience undesirable lift, which can diminish the sensation of being firmly planted on the road, or increased air turbulence, leading to greater noise intrusion and a less refined driving experience. Conversely, vehicles engineered with meticulously optimized aerodynamic profiles deliver a notably quieter, more stable, and consequently, a safer travel experience for occupants. This deep integration of aerodynamic principles into the fundamental attributes of a vehicle’s performance underscores its importance not merely for economic operation but for the entire spectrum of the driving experience across diverse road conditions.
The Future of Aerodynamic Innovation in Transport
The relentless global pursuit of enhanced efficiency and sustainability across all facets of mobility guarantees that aerodynamic innovation will remain a central and pivotal focus for the automotive industry. Future transport solutions, encompassing advanced urban mobility concepts, highly automated autonomous vehicles, and specialized commercial trucks, will increasingly prioritize aerodynamic optimization. This emphasis is driven by the necessity to comply with increasingly stringent environmental regulations and to meet evolving consumer and commercial demands for reduced operating costs and improved environmental footprints. Ongoing research continues to explore groundbreaking concepts such as active flow control, where minute jets or synthetic jets are employed to precisely manipulate airflow over vehicle surfaces, alongside more radical design paradigms that could fundamentally redefine the traditional shape and configuration of cars and trucks. Concurrently, manufacturing processes are undergoing significant evolution to facilitate the production of increasingly intricate and aerodynamically superior body structures, thereby ushering in a transformative era for the future of transport.
The foundational principles of vehicle aerodynamics are indispensable for achieving both superior fuel efficiency and enhanced driving performance across the entire scope of automotive engineering. From the conceptualization of initial designs to the integration of advanced technological solutions, the continuous and dedicated effort to minimize air resistance remains a primary catalyst for innovation within the industry. As the global imperative for sustainable transport solutions intensifies, the strategic role of aerodynamics will undoubtedly expand, fundamentally shaping the future trajectory of how vehicles are designed, operate, and consume energy on our roads worldwide.